Key takeaways:
- Optimized OR design enhances efficiency: standardized layouts and workflows improve safety, reduce errors, and enhance patient care.
- Technology transforms surgery: imaging, robotics, and hybrid ORs improve precision, reduce trauma, and enable remote collaboration.
- Flexibility ensures future readiness: adaptable ORs integrate new technologies, support evolving procedures, and reduce renovation costs.
Behind every successful surgery lies complex medical equipment and a team of highly skilled professionals. The operating rooms (ORs) where these procedures occur are equally complex, fast-paced, and demanding. They call for an immense amount of flexibility and a considerable amount of careful planning within their design. As hospitals reevaluate their post-pandemic utilization and needs, the perioperative environment requires optimized ORs now and in the future.
Planning Considerations
When designing a modern operating room, there are several factors to consider: optimal workflow, standardization, and quality and safety.
- Optimal Workflow. Streamlining workflows within the operating room is like organizing a well-choreographed dance where everyone knows their steps. Experienced designers will simulate life-size operating rooms to evaluate workflows with actual doctors and nurses to ensure optimization and foster better communication between surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and support staff.1 Workflow optimization requires thoughtful, hands-on planning to use resources and space efficiently, safely, and function well to deliver high-quality patient care.
- Standardization. Because most hospitals have multiple ORs, standardization is crucial because it guarantees that every room is set up and organized the same. Doctors and nurses know precisely where to find what they need when they move between ORs. This consistency saves time and minimizes mistakes, which is vital in keeping patients safe. Standardizing OR design also helps hospitals be more efficient because they know what equipment and supplies each room requires. Additionally, designing universal ORs using standardized design and room set-up aims for easier scheduling of ORs and increased throughput.
- Quality and Safety. Operating rooms are among the most critical hospital environments, and ensuring a safe experience for patients, surgeons, and staff is essential. Patients trust surgical teams with their well-being, while surgeons depend on meticulously controlled and well-equipped environments to perform procedures effectively. Prioritizing safety while maintaining a sterile environment with procedural accuracy is essential to mitigate risks and ensure optimal outcomes for everyone involved.2
While these factors are important, it’s also essential to understand the nuances and complexities of modern operating rooms. For example, general operating rooms differ from urology or orthopedic ORs. Each has different needs, including vastly different equipment and support systems with specific safety requirements. Designers must assess operating rooms individually and understand their goals before design begins.
Incorporating Innovative Technologies
The healthcare sector has historically been slower to embrace new technologies due to concerns about high implementation costs, uncertainty about patient benefits, regulatory hurdles, and data privacy.3 COVID-19 prompted a substantial disruption, particularly with the widespread adoption of telemedicine, which demanded a shift in approaches that embraced digital patient care. However, modern medical innovations have spiked in recent years, especially with the trends toward Artificial Intelligence (AI), augmented reality, robotics, and an emphasis on patient and staff experience.
.jpg)
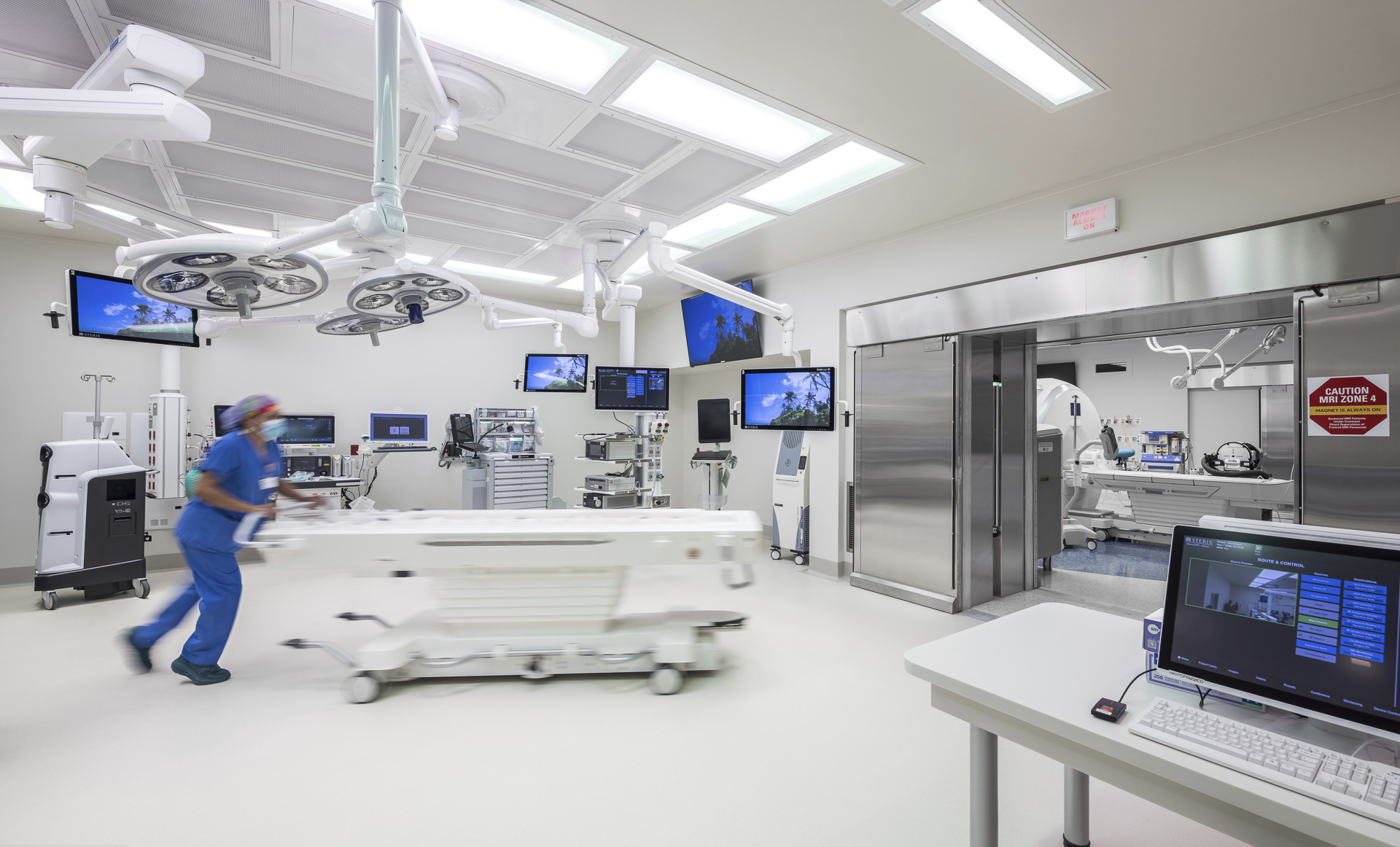
One significant development is the integration of advanced imaging modalities, which include technologies such as MRI, CT scans, and intraoperative ultrasounds. These technologies allow surgeons to visualize what they’re doing in real time, boosting accuracy and precision and leading to reduced patient trauma and faster recovery time.4 Robotic-assisted surgery has transformed the OR by enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with dexterity and control, particularly in confined spaces or delicate areas. Robotic surgery minimizes tissue damage, reduces blood loss, and promotes faster healing by adapting the surgeon's hand movements into precise micro-movements. Various surgical instruments can be connected to robotic arms, allowing surgeons to manipulate graspers and other equipment remotely. Remote connectivity technologies have also transformed our healthcare experience, especially following the COVID-19 pandemic. Through telepresence and video conferencing solutions, specialists can remotely participate in surgical procedures, providing real-time guidance and expertise to on-site teams. These techniques also make sharing information, such as medical images, patient data, and surgical plans, easier.
The implementation of hybrid operating rooms has also seen substantial growth due to these advancements and the increasing demand for integrated surgical solutions.5 Hybrid ORs combine traditional surgical facilities with advanced imaging and diagnostic capabilities, allowing for more efficient and versatile procedures. For example, UNC Health’s North Carolina Surgical Hospital, a seven-story, 375,000-square-foot building located in Chapel Hill, has recently added 26 new surgical suites that accommodate equipment for an improved patient care experience.
Four of these operating rooms are “hybrid rooms” that accommodate imaging technology and equipment, which means that traditionally invasive procedures can be less traumatic and more streamlined. Surgeons can, for example, make small incisions and use in-room imaging to perform delicate repairs on abdominal aortic aneurysms or bulges in the artery below the heart instead of the large chest incision used in traditional surgery.
Patient and Staff Experience
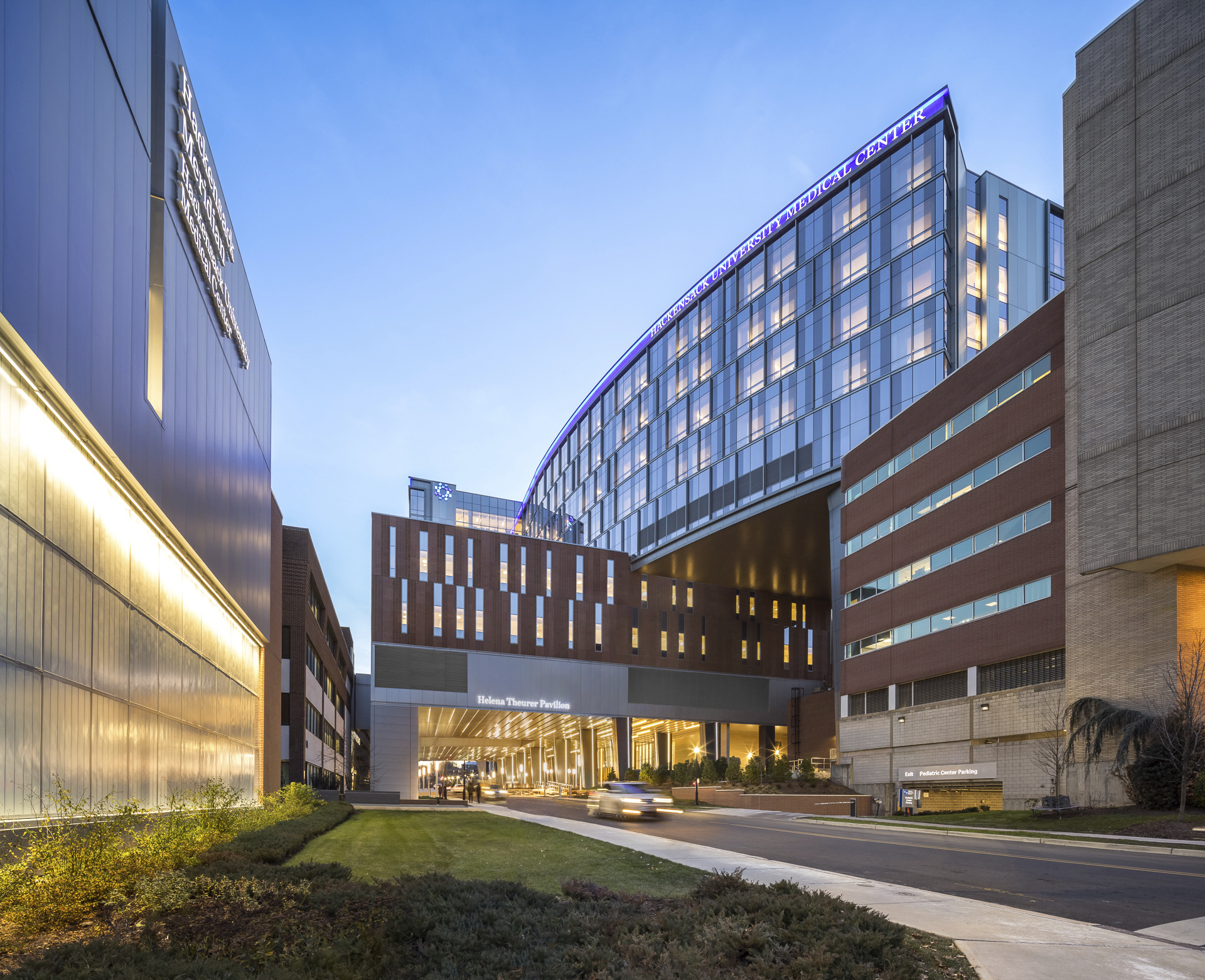
Efficient design enhances patient and staff experiences within a medical facility, incorporating aesthetically pleasing spaces while promoting healing, comfort, and emotional well-being.6,7 Hackensack Meridian Health, a leading not-for-profit healthcare organization based in New Jersey, is a prime example of designing for the patient experience.

The Helena Theurer Pavilion is a state-of-the-art, nine-story surgical and intensive care tower on the Hackensack University Medical Center campus in Hackensack, New Jersey. The goal was to create an environment that prioritizes patient and family comfort while creating an efficient workflow for staff.8 By organizing vertical circulation and separating staff elevators from patient elevators, the design optimizes wayfinding and keeps staff organized in the vast complex. The peri-operative platform features an innovative design with 24 ORs strategically distributed across two adjacent floors and 72 prep/recovery spaces. Distinguishing itself with cutting-edge advancements, the surgical suite integrates state-of-the-art technology, including an intraoperative MRI, redefining precision and efficiency in patient care. Additionally, creating a dual-purpose surgical suite, with separate areas for inpatient and outpatient procedures, ensures optimal utilization of resources, especially the rare intraoperative MRI, even when not actively used in surgery.
Futureproofing and Flexibility
Flexibility and futureproofing are vital in designing operating suites to support teams of specialists, accommodate future technological advances, and prepare for tomorrow’s unknown challenges.
By prioritizing flexibility, operating rooms can more easily integrate emerging technologies and adapt to evolving surgical procedures. Similarly, futureproofing enhances an operating room's longevity and contributes to its cost-effectiveness by reducing the frequency of significant renovations or equipment replacement.
Inherent in the process, designers need to consider scalability, compatibility with emerging industry standards, investments in durable equipment, and establishing processes for ongoing evaluation to identify emerging trends and opportunities for improvement.
Designing modern operating rooms requires careful planning, flexibility, and foresight. Current knowledge of healthcare technologies and equipment helps hospital operating rooms adapt to future innovations and the dynamic needs of medical professionals and patients.
References:
1. Oh Y, Gill S, Baek D, et al. Improving the Mental Health of Surgical Teams Through Operating Room Design. HERD: Health Environments Research & Design Journal. 2024;17(2):57-76. Available at: https://www.healthdesign.org/knowledge-repository/improving-mental-heal…
2. Buckner, L., Lacy, J., Young, K., & Dishman, D. Decreasing Foot Traffic in the Orthopedic Operating Room: A Narrative Review of the Literature. Journal of Patient Safety. 2022;18(2), e414–e423. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33871413/
3. Khan B, et al. Drawbacks of Artificial Intelligence and Their Potential Solutions in the Healthcare Sector. Biomed Mater Devices. 2023; Feb 8:1-8. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9908503/
4. Smith J. Advancements in Intraoperative Imaging for Guided Minimally Invasive Surgery. OMICS J Radiol. 2023;12: 501. Available at: https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/advancements-in-intraoperative-…. Clark M, Horton J. Hybrid Operating Room Suites: CADTH Horizon Scan. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; June 2023. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK595334/
6. Liu JC. How Design Affects Health. AMA J Ethics. 2024;26(12): E899-900. Available at: https://journalofethics.ama-assn.org/article/how-design-affects-health/…
7. Sangolli A, Doane R. Ambulatory Surgery Center Design with Patients and Staff in Mind. Health Facilities Today. February 23, 2023. Available at: https://www.healthcarefacilitiestoday.com/posts/Ambulatory-Surgery-Cent…
8. Gupta T, Sangolli A. Answering Challenges Creatively. Modern Construction & Design. 2023;19(5):31-35. Available at: https://lsc-pagepro.mydigitalpublication.com/publication/?i=801778&p=34…

